GC Low Dead Volume Injection Port Liners for Thermal Desorption
Description
These new Low Dead Volume Injection Port Liners have been specifically designed for use with the Scientific Instrument Services Short Path Thermal Desorption System but could also be utilized with other injection systems and techniques. It is designed to provide for a low dead volume injection port with uniform heat dissipation over the entire injection port length and also to provide for the maximum heat transfer to the injecting needle.
Conventional injection port liners are constructed of glass or quartz glass and normally have an inner diameter of 2.0 to 4.0 mm to allow for the vaporization and expansion of liquids when they are injected into the GC injection port. However when using the Thermal Desorption technique, the sample is being introduced in the gas phase and no expansion volume is required. In fact this expansion volume is a deterrent to optimum performance when using the Thermal Desorption technique. This dead volume around the syringe needle impedes optimum heat transfer from the injection port to the syringe needle. As a result the syringe needle is at a lower temperature than the injection port itself. For most compounds this is not a major problem, however when analyzing semi-volatiles or other higher molecular weight compounds it can pose limitations to the technique by causing these higher boiling compounds to condense in the syringe needle before they are introduced into the injection port. Also the glass liner itself is a poor conductor of heat to the sample or syringe needle. These problems are compounded in some instruments such as in the H.P. split/splitless injection port. In order to reduce septum bleed, these injection ports have a temperature differential of up to 100¡ from the middle of the injection port where the temperature is regulated to the top area of the injection port near the septum. This design feature can further complicate the Desorption of high boilers into the GC injection port by causing these semi-volatiles to condense in the syringe needle near the septum area of the injection port.
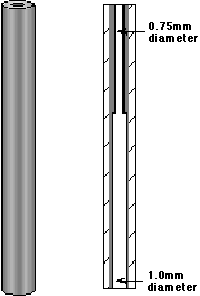
The new Low Dead Volume Injection Port Liners were designed to minimize or eliminate the shortcomings of the conventional Glass or Quartz injection port liners. The main body of the injection port liner is constructed of Glass Lined Stainless Steel Tubing. This stainless steel body provides for better heat transfer over the entire length of the injection port liner due to the improved thermal conductivity of the metal versus the glass liners. The glass liner is deactivated to minimize sample decomposition. The top half of the injection port liner has an inner diameter of 0.75 mm and closely fits around the injecting needle. This provides for the optimum transfer of heat from the injection port liner to the injecting needle eliminating cold spots in the syringe needle and enabling the transfer of higher boilers into the GC injection port. The bottom half of the injection port liner has an inner diameter of 1.0 mm to permit the introduction of samples from all types of syringe needles including the side port needles commonly used with the S.I.S. Thermal Desorption System. Both the upper and the lower inner surfaces of the injection port liner are glass lined. The net result is an injection port liner with low dead volume and good heat transfer to the injecting needle to permit the analysis of a wider range of compounds using the Short Path Thermal Desorption Technique.
Similar designs for other gas chromatographs are also available on request.
Features
- Low Dead Volume
- Maximum Heat Transfer to Injecting Needle
- Uniform Heat Transfer Over Entire Injection Port Length
- Increased Detection Level for Semi-volatiles
GLT Low Volume Injection Port Liners are ideal for Thermal Desorption and headspace GC injection.
 Purge and Trap Stainless Steel Purge Heads
Purge and Trap Stainless Steel Purge Heads  Thermal Desorption Sample Loader
Thermal Desorption Sample Loader  Short Path Thermal Desorption Accessories Supply Kit
Short Path Thermal Desorption Accessories Supply Kit  Seals for SIS Thermal Desorption Tubes
Seals for SIS Thermal Desorption Tubes  Short Path Thermal Desorption Tubes
Short Path Thermal Desorption Tubes  Aluminum Funnel for Loading Packings into Desorption Tubes
Aluminum Funnel for Loading Packings into Desorption Tubes  SIS Purge and Trap System
SIS Purge and Trap System  Small Sample Spatula
Small Sample Spatula  Needles for the Short Path Thermal Desorption System
Needles for the Short Path Thermal Desorption System  24 Tube Conditioning Oven for Thermal Desorption Tubes
24 Tube Conditioning Oven for Thermal Desorption Tubes  Thermal Desorption Conditioning Oven - 6 Tube
Thermal Desorption Conditioning Oven - 6 Tube